Are Endometriosis, Adenomyosis, and PCOS Autoimmune Conditions?
By Our Daughters Foundation
More and more women are asking an important question: Could my hormone-related illness also be connected to my immune system?
Conditions like endometriosis, adenomyosis, and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) are often discussed in the context of reproductive health or hormonal imbalance. But researchers are beginning to explore deeper connections—specifically, whether autoimmunity plays a role in these diseases.
Let’s break down what the science says—and what questions remain unanswered.
Are Endometriosis, Adenomyosis, and PCOS Autoimmune Conditions?
By Our Daughters Foundation
More and more women are asking an important question: Could my hormone-related illness also be connected to my immune system?
Conditions like endometriosis, adenomyosis, and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) are often discussed in the context of reproductive health or hormonal imbalance. But researchers are beginning to explore deeper connections—specifically, whether autoimmunity plays a role in these diseases.
Let’s break down what the science says—and what questions remain unanswered.
What Is Autoimmunity?
The immune system is designed to protect the body from threats like viruses and bacteria. But in autoimmune diseases, the immune system becomes misguided and starts attacking the body’s own cells and tissues.
Common autoimmune conditions include:
• Lupus
• Rheumatoid arthritis
• Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
• Multiple sclerosis
Symptoms vary widely, but many autoimmune conditions involve chronic inflammation, pain, fatigue, and a pattern of flare-ups.
The Immune System and Endometriosis
Endometriosis occurs when tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus—causing pain, inflammation, and sometimes infertility. While its exact cause is still debated, many researchers believe that the immune system fails to clear out these rogue cells effectively.
Several studies have found:
• Women with endometriosis often have higher levels of inflammatory markers, like cytokines and prostaglandins.
• Natural killer (NK) cell activity is lower in women with endometriosis, impairing the immune system’s ability to destroy misplaced cells.
• There are elevated autoantibodies in some patients, suggesting an autoimmune component.
Some scientists now consider endometriosis to be a non-classical autoimmune disease—showing many features of one without meeting all diagnostic criteria.
Further reading:
• NIH - Immune dysfunction in endometriosis: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30664929/
• Cleveland Clinic - Endometriosis and the Immune System: https://health.clevelandclinic.org/endometriosis-and-the-immune-system/
What About Adenomyosis?
Adenomyosis is sometimes called the "sister disease" of endometriosis. It occurs when endometrial tissue grows into the muscular wall of the uterus. It's less studied, but immune abnormalities have also been observed.
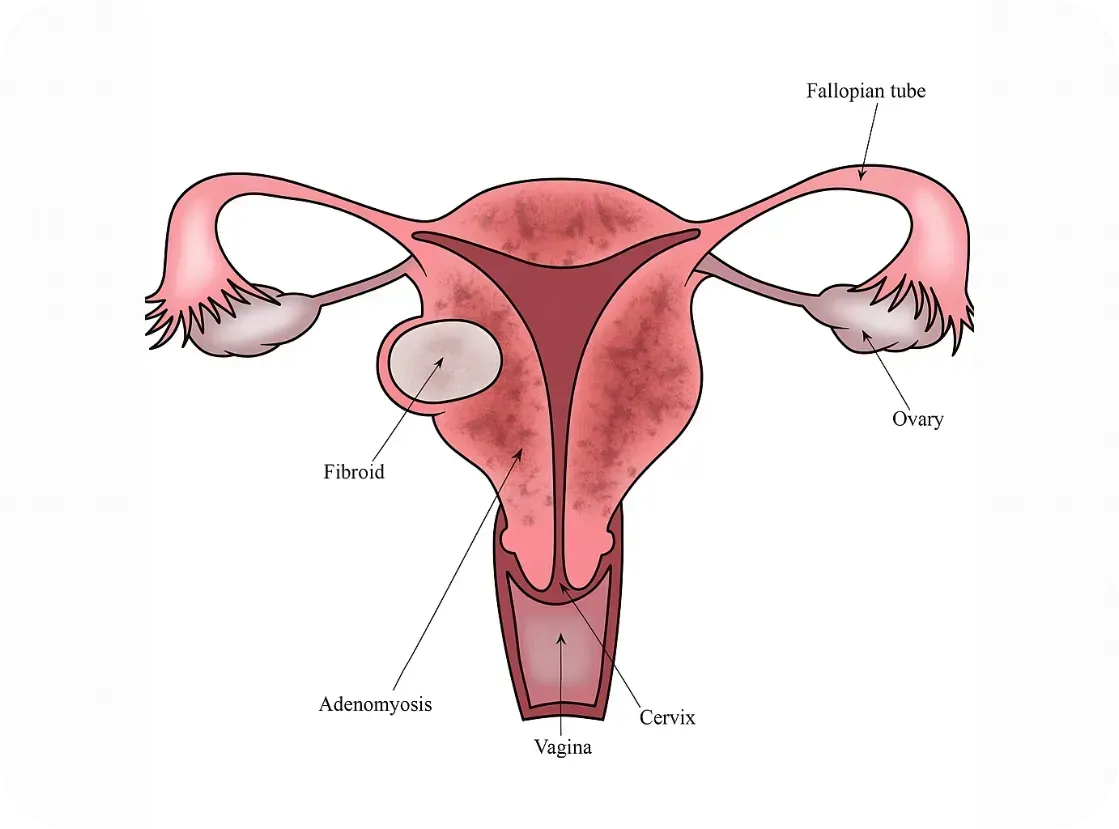
Research is still emerging, but here’s what we know:
• Women with adenomyosis show immune cell changes and chronic inflammation within the uterus.
• Some studies report increased macrophage and mast cell activity—cells involved in both immune defense and inflammation
• The condition often coexists with endometriosis, raising questions about shared immune pathways.
While it’s too early to label adenomyosis an autoimmune disorder, it may involve an immune imbalance that contributes to symptoms.
Further reading:
• Frontiers in Immunology - Immunopathogenesis of Adenomyosis: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2021.796273/full
PCOS and Autoimmune Overlap
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is primarily known as a hormonal disorder involving androgen excess and insulin resistance. However, there’s growing interest in its immune connections, especially in women with chronic inflammation or thyroid issues.
Emerging links include:
• Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (an autoimmune thyroid disorder) is more common in women with PCOS.
• Inflammatory markers like C-reactive protein (CRP) are often elevated in PCOS patients.
• Some PCOS patients have anti-ovarian antibodies, suggesting potential autoimmunity.
Still, the autoimmune theory is more speculative in PCOS than in endometriosis.
Further reading:
Further reading:
• Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism - PCOS and Autoimmune Disease: https://academic.oup.com/jcem/article/106/9/e3536/6280755
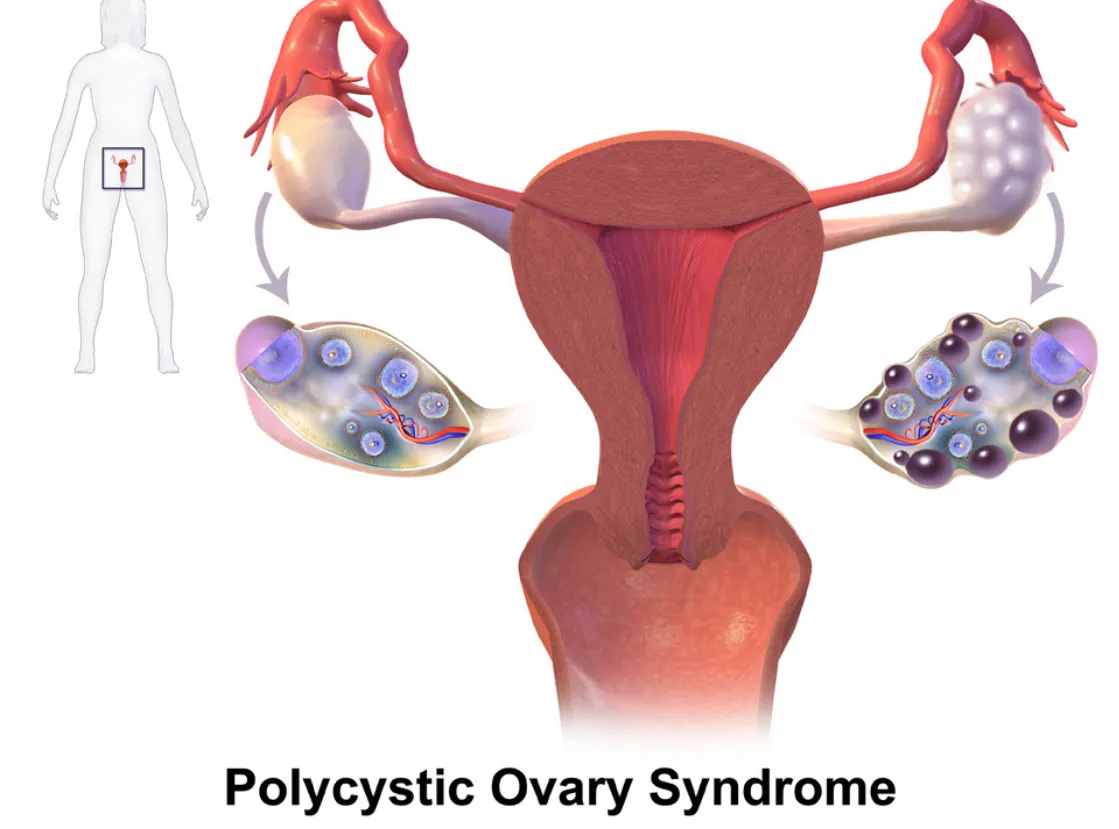
Why Does This Matter?
If immune dysfunction is part of the puzzle, treatment strategies may need to shift. Many women with endometriosis, adenomyosis, or PCOS are treated solely with hormone suppression—but if autoimmunity is involved, we may also need to address inflammation, gut health, and immune regulation.
There’s also hope that newer treatments—like immunomodulatory therapies or even personalized nutrition and lifestyle interventions—could improve outcomes when tailored to the immune system’s role.
Bottom Line
We don’t yet have all the answers, but the research is evolving. Endometriosis, adenomyosis, and PCOS may not be traditional autoimmune diseases—but they often coexist with immune dysfunction, and the overlap deserves attention. At Our Daughters Foundation, we believe in honoring women’s voices, advocating for deeper research, and pursuing whole-body solutions.
If you’ve experienced overlapping conditions like endo, thyroid disease, or unexplained inflammation—you’re not alone.
What Is Autoimmunity?
The immune system is designed to protect the body from threats like viruses and bacteria. But in autoimmune diseases, the immune system becomes misguided and starts attacking the body’s own cells and tissues.
Common autoimmune conditions include:
• Lupus
• Rheumatoid arthritis
• Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
• Multiple sclerosis
Symptoms vary widely, but many autoimmune conditions involve chronic inflammation, pain, fatigue, and a pattern of flare-ups.

The Immune System and Endometriosis
Endometriosis occurs when tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus—causing pain, inflammation, and sometimes infertility. While its exact cause is still debated, many researchers believe that the immune system fails to clear out these rogue cells effectively.
Several studies have found:
• Women with endometriosis often have higher levels of inflammatory markers, like cytokines and prostaglandins.
• Natural killer (NK) cell activity is lower in women with endometriosis, impairing the immune system’s ability to destroy misplaced cells.
• There are elevated autoantibodies in some patients, suggesting an autoimmune component.
Some scientists now consider endometriosis to be a non-classical autoimmune disease—showing many features of one without meeting all diagnostic criteria.
Further reading:
• NIH - Immune dysfunction in endometriosis: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30664929/
• Cleveland Clinic - Endometriosis and the Immune System: https://health.clevelandclinic.org/endometriosis-and-the-immune-system/
What About Adenomyosis?
Adenomyosis is sometimes called the "sister disease" of endometriosis. It occurs when endometrial tissue grows into the muscular wall of the uterus. It's less studied, but immune abnormalities have also been observed.

Research is still emerging, but here’s what we know:
• Women with adenomyosis show immune cell changes and chronic inflammation within the uterus.
• Some studies report increased macrophage and mast cell activity—cells involved in both immune defense and inflammation
• The condition often coexists with endometriosis, raising questions about shared immune pathways.
While it’s too early to label adenomyosis an autoimmune disorder, it may involve an immune imbalance that contributes to symptoms.
Further reading:
• Frontiers in Immunology - Immunopathogenesis of Adenomyosis: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2021.796273/full
PCOS and Autoimmune Overlap
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is primarily known as a hormonal disorder involving androgen excess and insulin resistance. However, there’s growing interest in its immune connections, especially in women with chronic inflammation or thyroid issues.
Emerging links include:
• Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (an autoimmune thyroid disorder) is more common in women with PCOS.
• Inflammatory markers like C-reactive protein (CRP) are often elevated in PCOS patients.
• Some PCOS patients have anti-ovarian antibodies, suggesting potential autoimmunity.
Still, the autoimmune theory is more speculative in PCOS than in endometriosis.
Further reading:
Further reading:
• Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism - PCOS and Autoimmune Disease: https://academic.oup.com/jcem/article/106/9/e3536/6280755

Why Does This Matter?
If immune dysfunction is part of the puzzle, treatment strategies may need to shift. Many women with endometriosis, adenomyosis, or PCOS are treated solely with hormone suppression—but if autoimmunity is involved, we may also need to address inflammation, gut health, and immune regulation.
There’s also hope that newer treatments—like immunomodulatory therapies or even personalized nutrition and lifestyle interventions—could improve outcomes when tailored to the immune system’s role.
Bottom Line
We don’t yet have all the answers, but the research is evolving. Endometriosis, adenomyosis, and PCOS may not be traditional autoimmune diseases—but they often coexist with immune dysfunction, and the overlap deserves attention. At Our Daughters Foundation, we believe in honoring women’s voices, advocating for deeper research, and pursuing whole-body solutions.
If you’ve experienced overlapping conditions like endo, thyroid disease, or unexplained inflammation—you’re not alone.
Join Us: Make a Difference Today
Your support can transform lives. Every donation helps us fund research, advocate for better care, and provide essential grants to women facing debilitating conditions.
Join Us: Make a Difference Today
Your support can transform lives. Every donation helps us fund research, advocate for better care, and provide essential grants to women facing debilitating conditions.

Follow the Money: We Can Do Better
The Gates Foundation just pledged $2.5 billion toward women’s health initiatives. But reading the accompanying article published in STAT points to the facts that the statistics for spending on R&D in ... ...more
Breaking News
August 08, 2025•5 min read

Neuroangiogenesis: Nerves & Blood Vessels Fueling Endo
Neuroangiogenesis—a mouthful of a word that simply means the simultaneous growth of new nerves (neuro-) and blood vessels (-angiogenesis). And it’s changing the way experts understand and treat endome... ...more
Breaking News
July 30, 2025•4 min read

Endometriosis: A Cancer-Mimicking Disease
Endometriosis: Why Scientists Say It Should Be Treated Like Cancer. It spreads like cancer; It grows its own blood supply; It avoids the body’s defenses; It messes with cell signals; It can increase c... ...more
Breaking News
July 17, 2025•3 min read

Endometriosis, Adenomyosis, and PCOS Autoimmune Conditions
Immune dysfunction: a key link in chronic conditions, impacting future treatment. ...more
Breaking News
July 17, 2025•3 min read

GUT FEELINGS: The Hidden Link Between Gut Health and Hormonal Imbalance
Discover the hidden links and how optimizing gut health can transform your well-being. ...more
Breaking News
July 17, 2025•2 min read

Breaking the Silence: Why Endometriosis Took So Long to Be Taken Seriously and What’s Finally Changing
For millions of women around the world, the story of endometriosis is one of pain, dismissal, and delay. But after decades of silence, the tide is beginning to turn. ...more
Endometriosis ,Breaking News
July 17, 2025•3 min read
