GUT FEELINGS: The Hidden Link Between Gut Health and Hormonal Imbalance
By Our Daughters Foundation
GUT FEELINGS: The Hidden Link Between Gut Health and Hormonal Imbalance
By Our Daughters Foundation
1. The Gut Microbiome: Your Internal Ecosystem
Your gut isn’t just a tube for digesting food. It’s home to trillions of bacteria that:
• Help break down food
• Make key nutrients (like B vitamins)
• Train your immune system
• And — importantly — regulate estrogen levels
This bacterial community is called the gut microbiome, and when it’s healthy and diverse, it supports balanced hormones. But when the microbiome is out of balance — a condition called dysbiosis — problems can arise.

2. Estrobolome: The Gut’s Hormone Filte
Inside the gut, a specific group of bacteria known as the estrobolome helps process estrogen. These bacteria produce enzymes (like beta-glucuronidase) that influence how much estrogen is reabsorbed into the bloodstream versus excreted.
When the estrobolome is overactive or underactive, it can lead to:
• Excess circulating estrogen → linked to endometriosis, fibroids, PMS, and breast tendernes
• Too little estrogen → contributing to mood changes, bone loss, and vaginal dryness
So a disrupted gut can directly amplify hormonal imbalances.
3. Inflammation: The Common Denominator
Both gut dysbiosis and endometriosis are associated with chronic inflammation. When the gut barrier is weakened (a condition sometimes called “leaky gut”), it allows inflammatory molecules to pass into the bloodstream. This triggers an immune response — and in people with endometriosis or PCOS, it can worsen pelvic pain, fatigue, and hormonal chaos.
4. What the Research Says
While this field is still developing, early studies have found:
• Women with endometriosis often have altered gut microbiomes compared to those without the condition. [Study: Ata et al., 2019, Scientific Reports]
• A high-fiber, plant-rich diet may help support a more balanced gut flora and improve estrogen metabolism. [Study: Fuhrman et al., 2004, Journal of Nutrition]
• Some researchers are exploring probiotic therapy as a future tool for managing hormone-related conditions.
5. What Can You Do?
You can’t fully control your hormones — but you can support your gut.
Here are some gut-friendly, hormone-supporting habits:
• Eat more fiber: vegetables, fruits, legumes, and seeds
• Avoid excessive sugar and processed foods
• Include fermented foods: yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi
• Consider a probiotic — talk to your provider first
• Manage stress — cortisol (the stress hormone) also affects gut balance
• Support liver detoxification (which works with your gut to clear estrogen): eat cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and cauliflower

Final Thoughts
The gut isn’t just about digestion — it’s a key player in how your body handles hormones, pain, and inflammation.
If you’re struggling with endometriosis, PCOS, or unexplained hormone symptoms, supporting your gut might be an empowering place to start.
Want to Learn More?
Here are some helpful articles and research:
• The Gut Microbiome and Estrogen Metabolism – NIH
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6471213/
• Gut Microbiota and Endometriosis – Scientific Reports
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-019-39645-2
• How the Gut Influences Hormones – Integrative Medicine Journal
1. The Gut Microbiome: Your Internal Ecosystem
Your gut isn’t just a tube for digesting food. It’s home to trillions of bacteria that:
• Help break down food
• Make key nutrients (like B vitamins)
• Train your immune system
• And — importantly — regulate estrogen levels
This bacterial community is called the gut microbiome, and when it’s healthy and diverse, it supports balanced hormones. But when the microbiome is out of balance — a condition called dysbiosis — problems can arise.

2. Estrobolome: The Gut’s Hormone Filte
Inside the gut, a specific group of bacteria known as the estrobolome helps process estrogen. These bacteria produce enzymes (like beta-glucuronidase) that influence how much estrogen is reabsorbed into the bloodstream versus excreted.
When the estrobolome is overactive or underactive, it can lead to:
• Excess circulating estrogen → linked to endometriosis, fibroids, PMS, and breast tendernes
• Too little estrogen → contributing to mood changes, bone loss, and vaginal dryness
So a disrupted gut can directly amplify hormonal imbalances.
3. Inflammation: The Common Denominator
Both gut dysbiosis and endometriosis are associated with chronic inflammation. When the gut barrier is weakened (a condition sometimes called “leaky gut”), it allows inflammatory molecules to pass into the bloodstream. This triggers an immune response — and in people with endometriosis or PCOS, it can worsen pelvic pain, fatigue, and hormonal chaos.

4. What the Research Says
While this field is still developing, early studies have found:
• Women with endometriosis often have altered gut microbiomes compared to those without the condition. [Study: Ata et al., 2019, Scientific Reports]
• A high-fiber, plant-rich diet may help support a more balanced gut flora and improve estrogen metabolism. [Study: Fuhrman et al., 2004, Journal of Nutrition]
• Some researchers are exploring probiotic therapy as a future tool for managing hormone-related conditions.
5. What Can You Do?
You can’t fully control your hormones — but you can support your gut.
Here are some gut-friendly, hormone-supporting habits:
• Eat more fiber: vegetables, fruits, legumes, and seeds
• Avoid excessive sugar and processed foods
• Include fermented foods: yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi
• Consider a probiotic — talk to your provider first
• Manage stress — cortisol (the stress hormone) also affects gut balance
• Support liver detoxification (which works with your gut to clear estrogen): eat cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and cauliflower

Final Thoughts
The gut isn’t just about digestion — it’s a key player in how your body handles hormones, pain, and inflammation.
If you’re struggling with endometriosis, PCOS, or unexplained hormone symptoms, supporting your gut might be an empowering place to start.
Want to Learn More?
Here are some helpful articles and research:
• The Gut Microbiome and Estrogen Metabolism – NIH
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6471213/
• Gut Microbiota and Endometriosis – Scientific Reports
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-019-39645-2
• How the Gut Influences Hormones – Integrative Medicine Journal
Join Us: Make a Difference Today
Your support can transform lives. Every donation helps us fund research, advocate for better care, and provide essential grants to women facing debilitating conditions.
Join Us: Make a Difference Today
Your support can transform lives. Every donation helps us fund research, advocate for better care, and provide essential grants to women facing debilitating conditions.
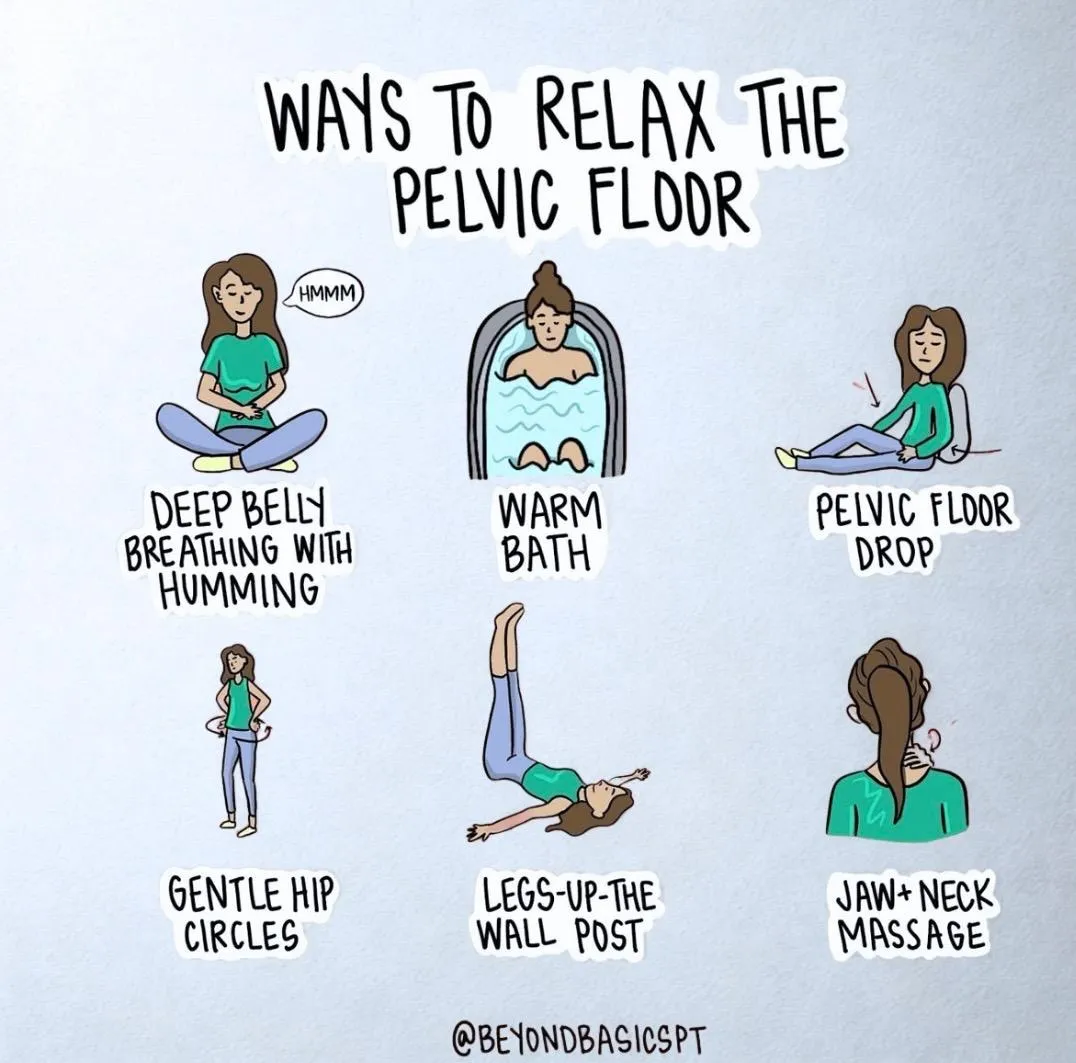
Relaxing Your Pelvic Floor
Relaxing the Pelvic Floor: Simple Practices with Powerful Benefits
Tension in the pelvic floor is more common than many realize—and it can be a significant source of pain, dysfunction, and stress. While most people have heard of Kegels to strengthen pelvic floor muscles, the equally important skill of relaxing those muscles is often overlooked. Chronic tightness in the pelvic floor can lead to a range of symptoms including pelvic pain, urinary urgency, painful intercourse, constipation, and low back pain.
*Your pelvic floor carries a lot—physically and emotionally. Incorporating simple tools like these into your daily routine isn’t just about relief after symptoms hit—it’s about building a system that might help prevent them before they start. A few minutes of deep breathing, gentle movement, or a warm bath can help calm your nervous system, ease tension, and support your body.That said, flare-ups aren’t always in your control—and that doesn’t mean you’re doing anything wrong. This is the nature of endometriosis. These are just supportive tools, not a cure—but sometimes, little things can make a big difference.
Fortunately, simple daily techniques—like the ones illustrated by @beyondbasicspt in the graphic above—can make a profound difference. Let’s break down each method and explore what the research says.
1. Deep Belly Breathing with Humming
Slow diaphragmatic breathing encourages the pelvic floor to relax naturally. When you inhale deeply, your diaphragm moves downward, and this movement is mirrored by the pelvic floor, creating a gentle stretch and release.
Why add humming? Humming stimulates the vagus nerve, which activates the parasympathetic nervous system (the “rest and digest” response), helping the entire pelvic region soften.
Research Insight: A 2020 study published in Pain Medicine found that slow, diaphragmatic breathing improved outcomes in patients with chronic pelvic pain by reducing muscle tone and improving nervous system regulation (Mehling et al., 2020).
2. Warm Bath
Immersion in warm water increases blood flow and reduces muscle guarding—especially in the pelvic area. The buoyancy also helps reduce gravitational compression, encouraging muscle relaxation.
Research Insight: Hydrotherapy has long been shown to reduce muscle tension and improve circulation (Kamioka et al., 2010). For pelvic pain specifically, warmth and hydrostatic pressure may help ease myofascial tension in the pelvic floor.
3. Pelvic Floor Drop (Let-Go Technique)
Unlike Kegels (which focus on contraction), the pelvic floor drop emphasizes releasing and lengthening the pelvic muscles. Think of it as the "exhale and let go" moment for the pelvic floor.
Research Insight: A 2016 review in the Journal of Bodywork and Movement Therapies emphasizes that relaxation techniques—including conscious "letting go"—are key in treating non-relaxing pelvic floor dysfunction (FitzGerald et al., 2016).
4. Gentle Hip Circles
These rhythmic movements help mobilize the hips and pelvis, gently loosening fascia and improving circulation in the pelvic region.
Research Insight: Movement therapies that increase pelvic mobility are beneficial in reducing hypertonicity (muscle overactivity) in the pelvic floor (Haugstad et al., 2006).
5. Legs-Up-The-Wall Pose
Known as Viparita Karani in yoga, this pose promotes venous return and encourages full-body relaxation. It also reduces pressure in the pelvic region and helps calm the nervous system.
Research Insight: A 2013 study in Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine noted that restorative yoga poses, like legs-up-the-wall, reduce sympathetic nervous system activity and improve muscle tone regulation (Telles et al., 2013).
6. Jaw + Neck Massage
Here’s a fascinating link: the jaw and the pelvic floor are neurologically and developmentally connected. Tension in one area often reflects or reinforces tension in the other.
Tip: Try gently massaging the base of your skull and jawline—or even releasing your tongue from the roof of your mouth—to help the pelvic muscles relax.
Research Insight: Somatic connections between the jaw and pelvis have been observed in body-oriented therapies. A 2021 review published in Medical Hypotheses proposed shared motor control pathways that link craniofacial and pelvic floor muscle groups (Wallden, 2021).
Final Thoughts
Pelvic floor relaxation isn’t just about relieving pain—it’s about restoring balance, function, and a sense of ease in the body. Whether you’re dealing with pelvic pain, recovering from childbirth, or simply seeking more mind-body awareness, these gentle practices are worth integrating into your daily routine.
As always, if you're experiencing persistent pelvic discomfort, consult a pelvic floor physical therapist for a personalized plan. These professionals can guide you through both strengthening and relaxation techniques safely.
References
Mehling, W. E., et al. (2020). Effects of breathing retraining on chronic pelvic pain. Pain Medicine, 21(4), 798–808.
Kamioka, H., et al. (2010). Effectiveness of aquatic exercise and balneotherapy: A summary of systematic reviews. Journal of Epidemiology, 20(1), 2–12.
FitzGerald, M. P., et al. (2016). Evaluation and treatment of non-relaxing pelvic floor dysfunction. J Bodyw Mov Ther, 20(2), 275–281.
Haugstad, G. K., et al. (2006). Muscular and non-muscular responses to movement therapy in women with chronic pelvic pain. Physiotherapy Research International, 11(4), 217–228.
Telles, S., et al. (2013). Restorative yoga for women with pelvic pain: a randomized controlled trial. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2013, 792581.
Wallden, M. (2021). The anatomical and neurobiological link between the jaw and pelvic floor. Medical Hypotheses, 150, 110556.
